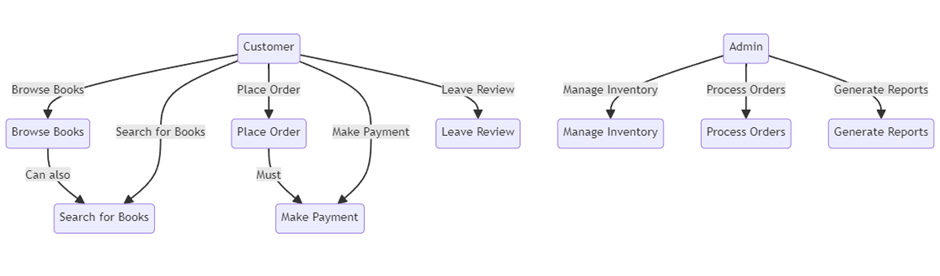
Hybrid Model for Monorepo and Polyrepo
Mix of Monorepo and Polyrepo in an Organization
Hybrid repository strategies combine elements of both
monorepo and polyrepo approaches to take advantage of their respective
strengths while mitigating their weaknesses. Here are some strategies for
adopting a hybrid approach:
- Monorepo
for Core Shared Code:
- Use
a monorepo for shared libraries, common components, and infrastructure
code that are critical across various projects.
- This
approach ensures consistent versioning and easy code sharing for
foundational components.
- Polyrepo
for Project-Specific Code:
- Create
separate repositories for project-specific code, applications, or
services.
- Each
project's repository contains its own codebase, dependencies, and version
control, providing autonomy for project teams.
- Dependency
Management:
- Establish
a clear and well-documented process for managing dependencies between the
monorepo and polyrepos.
- Use
dependency management tools like package managers (e.g., npm, yarn, or
pip) or Git submodules to include shared code from the monorepo into the
polyrepos.
- Continuous
Integration and Delivery (CI/CD):
- Implement
CI/CD pipelines that build and test code from both monorepo and
polyrepos.
- Ensure
that changes in shared code trigger automated testing and deployment
across relevant projects.
- Release
and Versioning Strategies:
- Define
consistent versioning and release strategies for the monorepo and
individual polyrepos.
- Document
these strategies and ensure that teams follow them consistently.
- Code
Ownership and Collaboration:
- Clearly
define code ownership and collaboration guidelines.
- Specify
which teams are responsible for maintaining shared code in the monorepo
and how they collaborate with project-specific teams.
- Tooling
and Automation:
- Invest
in tools and automation to streamline the integration of code between the
monorepo and polyrepos.
- Automate
the detection and resolution of code conflicts and compatibility issues.
- Documentation
and Onboarding:
- Create
thorough documentation to help new team members understand the hybrid
approach and the workflow.
- Provide
training and onboarding resources to ensure that everyone follows best
practices.
- Regular
Communication:
- Foster
open and frequent communication between teams working with the monorepo
and those maintaining polyrepos.
- Hold
regular meetings to discuss changes, updates, and challenges.
- Monitoring
and Metrics:
- Implement
monitoring and metrics to track the performance and health of the hybrid
setup.
- Use
these insights to make continuous improvements.
Hybrid repository strategies can be a flexible solution for
organizations with diverse needs. They allow you to balance the benefits of
code sharing and consistency while providing project-specific independence and
modularity. However, they require careful planning, documentation, and ongoing
coordination to be successful.
Ways for changes in monorepo to be notified to dependent projects hosted in polyrepo:
- Automated
Build and Deployment Pipelines:
- Implement
automated build and deployment pipelines for both the monorepo and the
polyrepos.
- Whenever
changes are made in the monorepo, the pipeline should trigger builds and
tests for the shared components.
- Upon
successful build and testing, the artifacts can be published or made
available for consumption by the projects in the polyrepos.
- The
project in the polyrepo can be configured to automatically pull or update
the shared components when new versions are published.
- Dependency
Management Tools:
- Use
dependency management tools, such as package managers (e.g., npm, yarn,
or pip), to specify dependencies on the shared components hosted in the
monorepo.
- Whenever
there's a new version of a shared component in the monorepo, the project
in the polyrepo can update its dependency version.
- Regularly run commands like npm install or yarn upgrade in the polyrepo project to fetch the latest versions of dependencies for nest.js, node.js, express.js projects.
- Dependency management in Visual Studio typically involves the use of the NuGet package manager for .NET projects. NuGet is a package manager that simplifies the process of adding, updating, and managing third-party libraries and dependencies within your .NET projects.
- Webhooks
and Notifications:
- Set
up webhooks or notifications in the monorepo's version control system or
in your CI/CD platform to inform the polyrepo project when changes occur.
- These
notifications can trigger actions in the polyrepo, such as initiating an
update process.
- Periodic
Synchronization:
- Implement
a scheduled job that periodically checks for changes in the monorepo and
updates the polyrepo accordingly.
- This
approach is useful when continuous integration or automated processes are
not feasible.
- Manual
Triggering:
- Have
a defined process for team members to manually trigger updates in the
polyrepo project whenever they make changes to shared code in the
monorepo.
- This
manual step ensures control and awareness of when updates are applied.
- Change
Logs and Release Notes:
- Maintain
detailed change logs and release notes for the shared components in the
monorepo.
- The
polyrepo project can periodically check these logs to determine if there
are new updates or changes it needs to incorporate.
The approach you choose will depend on your specific use
case, tools, and infrastructure. Many organizations combine multiple methods to
ensure that polyrepo projects stay up to date with changes in the monorepo.
Regardless of the approach, clear documentation and communication are essential
to keep all team members informed about the processes and responsibilities for
managing dependencies between the monorepo and polyrepos.
Comments
Post a Comment